How Can a Digital Nomad Declare Himself Non Resident and Pay Zero Tax
The digital nomad lifestyle, characterized by remote work from diverse global locations, has captured the imagination of modern professionals seeking unparalleled freedom. Yet, for non-resident digital nomads, a compelling aspect lies in the pursuit of minimizing or even eliminating taxes through lawful means. This exploration delves into the intricate world of international tax laws, unraveling strategies, and considerations that enable digital nomads to navigate the complexity and legally reduce their tax burdens.
How Can a Digital Nomad Declare Himself Non Resident and Pay Zero Taxes?
Becoming a non-resident and paying zero taxes as a digital nomad is an enticing prospect, but it involves careful planning and adherence to tax laws. Here are five ways to achieve this:
Establish a Tax Residency Elsewhere
To declare yourself a non-resident for tax purposes, you'll need to establish tax residency in a country that has favorable tax laws for non-residents. This typically involves spending a significant portion of the year (usually less than 183 days) in that country and demonstrating economic ties, such as renting or owning property, and having a local bank account. Popular choices for digital nomads include countries like Panama, Portugal, and the UAE, which offer tax incentives for foreign residents.
A non-US resident can pay zero taxes in Delaware by setting up his business in a zero-tax state such as Delaware, and if you're a digital nomad without an active residence, these earnings won't be taxable as you won't be eligible for taxes in another country.
Corporate Income Tax FAQs - Delaware Division of RevenueIf you're following this scheme, or another, don't forget to get properly covered by a nomad insurance as you will have to leave your home and host countries local social security and coverage schemes.
Utilize Tax Treaties
Many countries have tax treaties in place to prevent double taxation. These treaties often define tax residency and provide mechanisms for determining where you should pay taxes. By understanding and leveraging these treaties, you can potentially avoid paying taxes in multiple countries. For instance, if you're a U.S. citizen, the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows you to exclude a certain amount of your income from U.S. taxation if you qualify as a bona fide resident of another country.
Create a Tax-Efficient Business Structure
Establishing a tax-efficient business structure, such as a limited liability company (LLC) or offshore corporation, can help reduce your tax liability. Some countries, like Singapore and Hong Kong, offer favorable tax regimes for businesses, making them attractive locations for registering your digital nomad venture. Income generated through your business can be structured in a way that minimizes your personal tax liability.
Monitor Your Physical Presence
Many countries have strict rules regarding the number of days you can spend within their borders without becoming a tax resident. Keeping meticulous records of your travel and ensuring you don't exceed the allowed days in a particular country is crucial. Some digital nomads use visa-free or visa-on-arrival travel arrangements to extend their stays, while still maintaining non-resident status for tax purposes.
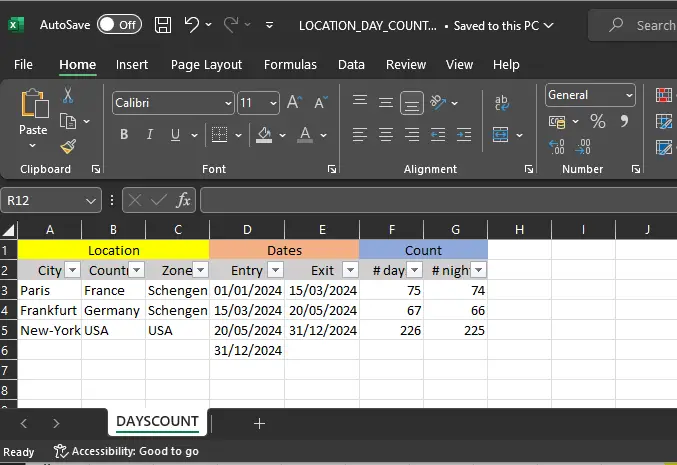
You can keep track of your physical presence using a simple spreadsheet tracker, on which you will record your entry and exit dates in any location you visit over a defined period of time, to make sure that you don't spend more than 183 days per calendar year in a given place.
Otherwise you might become defacto a tax payer by staying 183 days due to stay length which as more than half a year - and also that you do not overstay any visa.
Seek Professional Advice
Tax laws are complex and can change frequently. To navigate them successfully and ensure compliance, consider seeking the expertise of a tax professional or accountant who specializes in international tax matters. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, helping you make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that these strategies can help digital nomads reduce their tax liability, it is essential to note that paying 0% taxes may not always be possible or legal. Tax evasion is prohibited and carries severe penalties, including fines and jail time. Therefore, maintaining transparency with tax authorities and abiding by the laws of the countries you visit or reside in is essential. In addition, tax laws differ considerably from country to country, so what works for one digital nomad may not work for another. As a digital nomad, you should always seek professional advice and remain informed about tax regulations to ensure compliance while minimizing your tax burden.